Two-factor authentication (2FA): A short guide
Online security is no longer something optional. Data leaks, phishing, and credential theft happen every day, and once your password is exposed, attackers can easily try it on other platforms you use. Two-factor authentication (2FA) is a simple and effective way to protect yourself from this risk by adding an additional verification step every time you log in.

What is two-factor authentication?
Two-factor authentication, or 2FA, is a method that strengthens account security by verifying your identity through two independent factors. Instead of relying solely on a password — something you know — it also requires something you have (like your smartphone or a security token) or something you are (like your fingerprint or facial scan).
When logging in, you must complete both steps successfully. Even if cybercriminals steal your password, they can’t log in without the second authentication factor.
The most common types of two-factor authentication include:
- Email codes: One-time verification codes sent to your registered email.
- SMS verification: Numeric codes delivered via text message.
- Authenticator apps: Secure applications like Google Authenticator, Authy, or Microsoft Authenticator that generate short-lived codes.
- Push notifications: Approve or deny login attempts directly from your device.
- Hardware tokens: USB keys or physical devices that must be connected to confirm access.
All these methods achieve the same goal: ensuring that only you can access your account.
Why 2FA is essential for online security
Passwords alone are no longer enough to keep you safe online. Many users reuse them across different platforms, making it easy for attackers to exploit leaked credentials. Even complex passwords can be stolen through phishing, malware, or database breaches.
Enabling 2FA drastically reduces the risk of hacking because attackers would still need your second authentication method, usually your phone or verification app.
For organizations, two-factor authentication is critical for data protection, securing internal communications, documents, and customer records. For individuals, it safeguards personal emails, social media, financial accounts, and cloud storage. Whether for business or personal use, 2FA acts as an effective shield against identity theft and unauthorized access.
Benefits and limitations of two-factor authentication
Main advantages:
- Strong protection against password theft: Even if your password is compromised, attackers need your second factor.
- Higher user trust: Platforms that support 2FA are seen as more reliable and security-conscious.
- Universal compatibility: Works with most operating systems, apps, and online services.
Possible limitations:
- Device dependency: Losing your phone or email access can temporarily block you from logging in.
- Phishing risks: Some attackers create fake 2FA screens to trick users into entering codes.
- Slight inconvenience: 2FA adds a few seconds to sign in: a small trade-off for vastly improved security.
If you ever lose access to your device, most platforms provide recovery codes or verified account restoration methods to help you regain control safely.
Best practices for using 2FA safely
To make the most of two-factor authentication, follow these key practices:
- Use authenticator apps instead of SMS: text messages can be intercepted during SIM-swapping attacks.
- Store recovery codes in a safe place to restore access if your phone is lost or replaced.
- Secure your phone and email with strong passwords and lock screens.
- Regularly review active sessions and devices in your account settings to detect suspicious logins.
- Never approve unexpected login prompts. If you receive a verification code without trying to log in, change your password immediately.
How 2FA works in practice
As an example, let’s look at ONLYOFFICE DocSpace, a collaborative platform for sharing and editing documents securely.
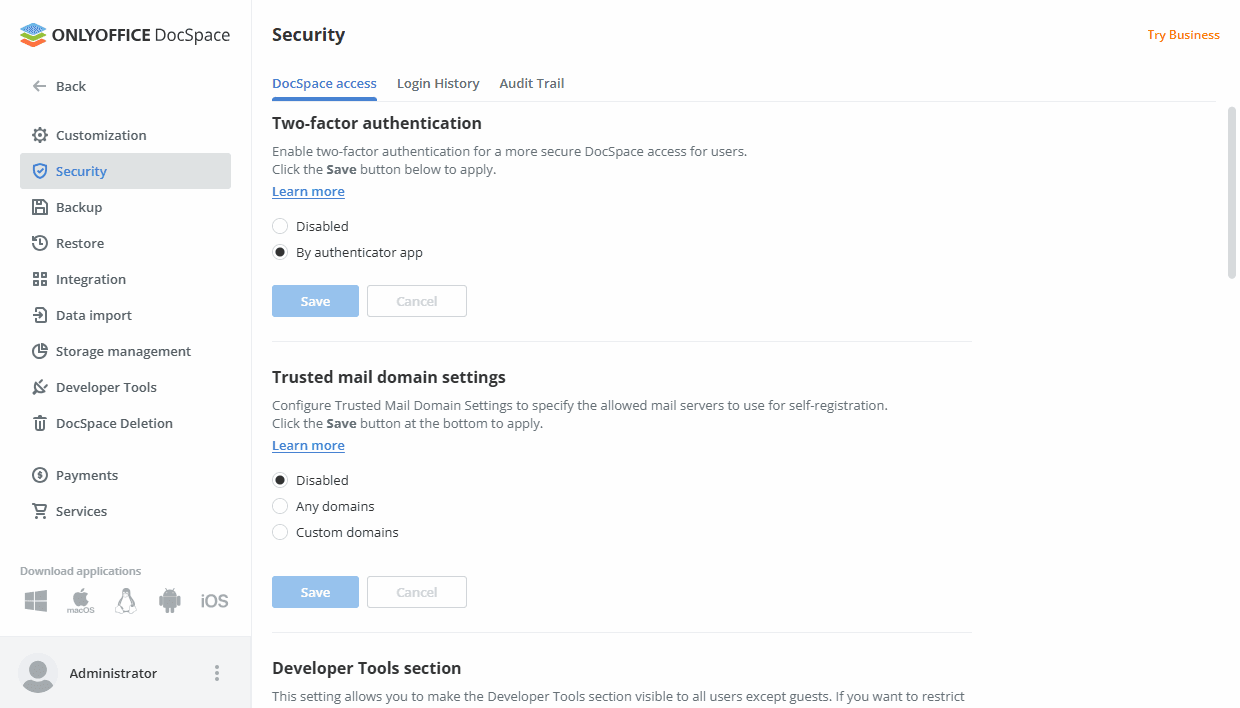
To prevent unauthorized access, users can enable two-factor authentication in their profile settings.
1. Open the Options menu in the lower-left corner and select Settings.
2. In the settings panel, go to the Security section.
3. Find the Two-factor authentication area.
4. Choose By authenticator app and click Save.
After activation, logging into DocSpace involves two steps:
1. Entering your password as usual.
2. Confirming your identity with a one-time verification code generated by your preferred app.

The first time you sign in after enabling 2FA, you’ll see a QR code and secret key on the confirmation page.
To complete setup:
1. Install an authenticator app on your mobile device (for example, Google Authenticator for Android or iOS).
2. Scan the QR code or manually enter the secret key.
3. Enter the six-digit code generated by the app and click Connect app.
This extra layer of protection only takes a few seconds but significantly increases account security. Even if your password is leaked, no one can access your workspace without your second factor.
Learn more about security in DocSpace.
Get ONLYOFFICE DocSpace and keep your documents safe
Add an extra layer of protection with two-factor authentication and secure every login.
Conclusion
Two-factor authentication is one of the simplest yet most powerful defenses against unauthorized access. It doesn’t require any special hardware or technical skills, but just a few minutes to enable it.
No matter which platform or app you are using, enabling 2FA should be a non-negotiable step in your digital routine. It’s a small habit that can prevent big problems.
Create your free ONLYOFFICE account
View, edit and collaborate on docs, sheets, slides, forms, and PDF files online.